Society Registration

What is Society?
The Societies Registration Act, 1860 was introduced for promotion of literature, science or fine arts, advancement of literature or for diffusion of useful knowledge for charitable purposes. It provides the procedure for society registration and operation in India.The society registration act, 1860 has been accepted by several state governments without or with further amendments.
- A society is an association of several individuals combined together by mutual consent to govern and act mutually for some communal purpose. Societies are intended to register for the charitable purpose like sports, music, culture, religion, art, education, etc.
- The formation of Society required minimum of seven or more persons and persons from India, Outside India, companies and other registered societies can also become the part of a society.
- Societies can also be registered or unregistered and only registered Societies can hold vested properties and/or have a suit filed by or against the Society.
- The application for registration of society must be made to the concerned authority in the State as it is amatter of concern State Governmentsin which the registered office of the Society is situated.


Purpose of Society Registration specified by the Societies Act, 1860
- Promotion of fine arts
- Diffusion of political education
- Grant of charitable assistance
- Promotion of science and literature
- Creation of military orphan funds
- Maintenance or foundation of galleries or public museum
- Maintenance or foundation of reading rooms or libraries
- Promotion or diffusion or instruction of useful knowledge
In addition to the above purposes specified by the Societies Act, 1860, a Society can also be registered for other purposes based on the amendment that has been enacted to the Societies Act, 1860 by the concerned State Government.
Process of Society Registration
- Step:1 Selection of a Name: To register a Society, the founding members must first agree on a name for the Society Name and it should be unique and not be the same as society previously registered as it would not be allowed.Further the proposed name for the society must not suggest patronage of the Government of India or any State Government or attract the provisions of Emblem and Names Act, 1950.
- Step:2 Byelaws of Society Registration -Niyamawali: It is like Memorandum & Article of Association.It contains rules and regulations of society and must be signed by each of the founding members & witness. It also contains details of all the members (atleast seven members) including their father’s name, designation address, occupation. The Niyamawali includes the following clauses:
1. Name clause
2. Registered office clause
3. Eligibility Criteria for membership
4. Object clause
5. Membership clause
6. Subscription clause
7. Meetings clause (Annual & Extra ordinary General Meeting)
8. Committee/ Governing body clause
9. Right & duties of Governing body
10. Validity of Society
11. Amendment clause
12. Dissolution clause
13. Cancellation of membership
14. Dispute clause
These seven members are collectively called the governing body which control the functioning of society and these members are elected for specific period and then re-elected through elections.
Governing body of society includes the following designation with their function:
1. Office bearer of executive body as PRESIDENT: Conduct all the meeting and co -ordinate with vice president regarding sitting arrangement of all the members of the meeting and deciding the place and date of meeting. In case of equal voted by the other members President have power of casting vote means the decision will be finalized by the vote of President.
2. VICE PRESIDENT: To take in charge of society work in the absence of President and will have all the right of president in the absence of president and vice president will arrange meeting and look for sitting arrangement for all the members of the meeting.
3. GENERAL SECRETARY: General Secretary has the power to sanction an amount as prescribed at a time that means no expense can be occurred until the permission from General Secretary is obtained.
4. JOINT SECRETARY: To take in charge of all the duties of General Secretary in the absence of General Secretary.
5. TRESURERAR: To maintain detailed and complete records of the funds of the society and to grant for expense as approved by General Secretary.
6. MEMBERS– (Minimum two members): Right to vote in the decision making of the society. - Step 3: Filling of Application:The signed Memorandum (Niyamawali) and Rules and Regulations must be filed with the requisite documents to be uploaded to concerned Registrar of Societies in the State with the prescribed fee. If the Registrar is satisfied with application for Society Registration and all details are true and correct in all respect, thenRegistrar would issue the registration certificate of society, and in case any discrepancy found then it comes for resubmission of application and need to file again with suggestive remarks.
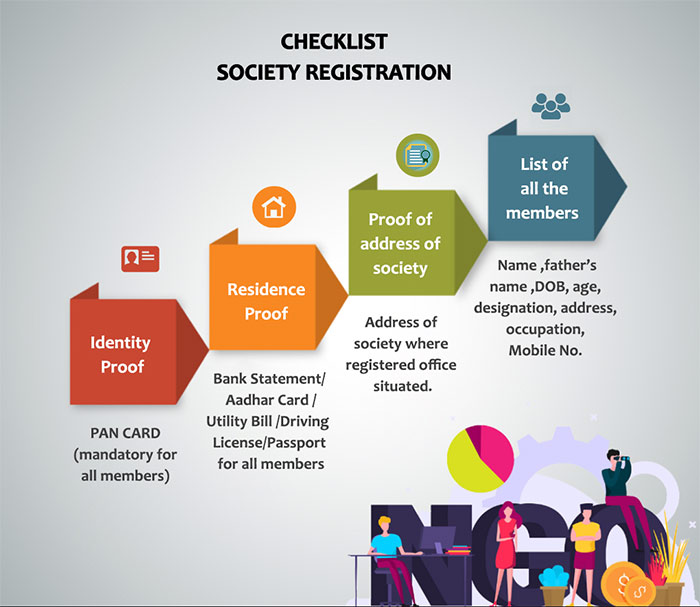

Documents required for Society Registration
- PAN CARD (mandatory for all members)
- The Residence Proof - Bank Statement/ Aadhar Card /Utility Bill /Driving License/Passport for all members
- Niyamawali
- Proof of address of society – address of society where located with NOC of landlord
- A list of all the members with their name ,fathers name ,designation, address, occupation and be signed by all the members.
Society Registration Government Fees (M.P.)
- Cyber treasury challan of Rs. 3000 in normal cases and in case of urgent registration, cyber treasury challan of Rs. 5000
- (government fees may vary from state to state.)
- M.P. online portal Fees: Rs. 100


Taxation of Society Registration
- It can apply for 80G and 12AA i.e. Tax exemption certificates after completing 3 year of NGO where donation received by NGO will be tax free and the person who is donating will get certificate for tax exemption.
Due Dates of Society Registration
- In case where audit is not required then the due date is 31st July of the assessment Year.
- In case audit is required to be conducted then 30th September of assessment Year.


Advantages of Society Registration
- Easy to form and the simplest registration out of the three option available for NGO i.e. Society/ Section 8 Company/ Trust.
- It can apply for 80G and 12AA i.e. Tax exemption certificates after completing 3 year of NGO where donation received by NGO will be tax free and the person who is donating will get certificate for tax exemption.
- It incur least registration cost as compared to Trust & Section 8 Company.
- Society has easy postincorporation compliance.

What is Society?
A society is an association of several individuals combined together by mutual consent to govern and act mutually for some communal purpose. Societies are intended to register for the charitable purpose like sports, music, culture, religion, art, education, etc. Societies can be registered or unregistered and only registered Societies can hold vested properties and/or have a suit filed by or against the Society.
What is purpose of Society?
- Promotion of fine arts
- Diffusion of political education
- Grant of charitable assistance
- Promotion of science and literature
- Creation of military orphan funds
- Maintenance or foundation of galleries or public museum
- Maintenance or foundation of reading rooms or libraries
- Promotion or diffusion or instruction of useful knowledge
In addition to the above purposes specified by the Societies Act, 1860, a Society can also be registered for other purposes based on the amendment that has been enacted to the Societies Act, 1860 by the concerned State Government.
What are the steps for registration of Society?
- Step:1 Selection of a Name: To register a Society, the founding members must first agree on a name for the Society Name and it should be unique and not be the same as society previously registered as it would not be allowed.Further the proposed name for the society must not suggest patronage of the Government of India or any State Government or attract the provisions of Emblem and Names Act, 1950.
- Step:2 Byelaws of Society Registration -Niyamawali: It is like Memorandum & Article of Association.It contains rules and regulations of society and must be signed by each of the founding members & witness. It also contains details of all the members (atleast seven members) including their father’s name, designation address, occupation.
- Step 3: Filling of Application:The signed Memorandum (Niyamawali) and Rules and Regulations must be filed with the requisite documents to be uploaded to concerned Registrar of Societies in the State with the prescribed fee. If the Registrar is satisfied with application for Society Registration and all details are true and correct in all respect, thenRegistrar would issue the registration certificate of society, and in case any discrepancy found then it comes for resubmission of application and need to file again with suggestive remarks.
What are the elements for Bye-Laws (Niyamawali) of Society registration?
1. Name clause
2. Registered office clause
3. Eligibility Criteria for membership
4. Object clause
5. Membership clause
6. Subscription clause
7. Meetings clause (Annual & Extra ordinary General Meeting)
8. Committee/ Governing body clause
9. Right & duties of Governing body
10. Validity of Society
11. Amendment clause
12. Dissolution clause
13. Cancellation of membership
14. Dispute clause
Who are governing body and functions of members of the governing body of the Society?
These seven members are collectively called the governing body which control the functioning of society and these members are elected for specific period and then re-elected through elections.
Governing body of society includes the following designation with their function:
1. Office bearer of executive body as PRESIDENT: Conduct all the meeting and co -ordinate with vice president regarding sitting arrangement of all the members of the meeting and deciding the place and date of meeting. In case of equal voted by the other members President have power of casting vote means the decision will be finalized by the vote of President.
2. VICE PRESIDENT: To take in charge of society work in the absence of President and will have all the right of president in the absence of president and vice president will arrange meeting and look for sitting arrangement for all the members of the meeting.
3. GENERAL SECRETARY: General Secretary has the power to sanction an amount as prescribed at a time that means no expense can be occurred until the permission from General Secretary is obtained.
4. JOINT SECRETARY: To take in charge of all the duties of General Secretary in the absence of General Secretary.
5. TRESURERAR: To maintain detailed and complete records of the funds of the society and to grant for expense as approved by General Secretary.
6. MEMBERS– (Minimum two members): Right to vote in the decision making of the society.
What is the provision of income tax for Society?
It can apply for 80G and 12AA i.e. Tax exemption certificates after completing 3 year of NGO where donation received by NGO will be tax free and the person who is donating will get certificate for tax exemption.
What are the due dates for the audit of Society?
- In case where audit is not required then the due date is 31st July of the assessment Year.
- In case audit is required to be conducted then 30th September of assessment Year.
What are the advantages of Society?
- Easy to form and the simplest registration out of the three option available for NGO i.e. Society/ Section 8 Company/ Trust.
- It can apply for 80G and 12AA i.e. Tax exemption certificates after completing 3 year of NGO where donation received by NGO will be tax free and the person who is donating will get certificate for tax exemption.
- It incur least registration cost as compared to Trust & Section 8 Company.
- Society has easy postincorporation compliance.
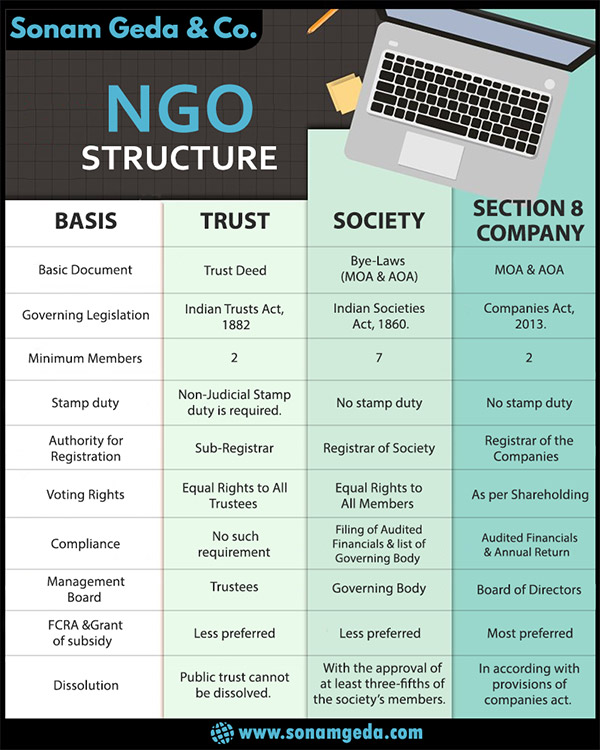
What is difference between Society and different form of organisation?
We have prepared a detailed and easy to understand comparative table showing availability of features and advantages of one form of business to that of others. The same can be found at the end of this page.
Who can be a member of the Society?
Member of society can include below mentioned persons:
- An individual, a firm, a company or a body corporate, registered under any law for the time being in force;
- The State Government or the Central Government;
- A local authority;
- A public trust registered under any law for the time being in force etc.
Videos on NGO-Society
To view video, click on image
Other Related Videos
To view video, click on image
Subscribe Our Newsletter
Get useful latest news & other important update on your email.